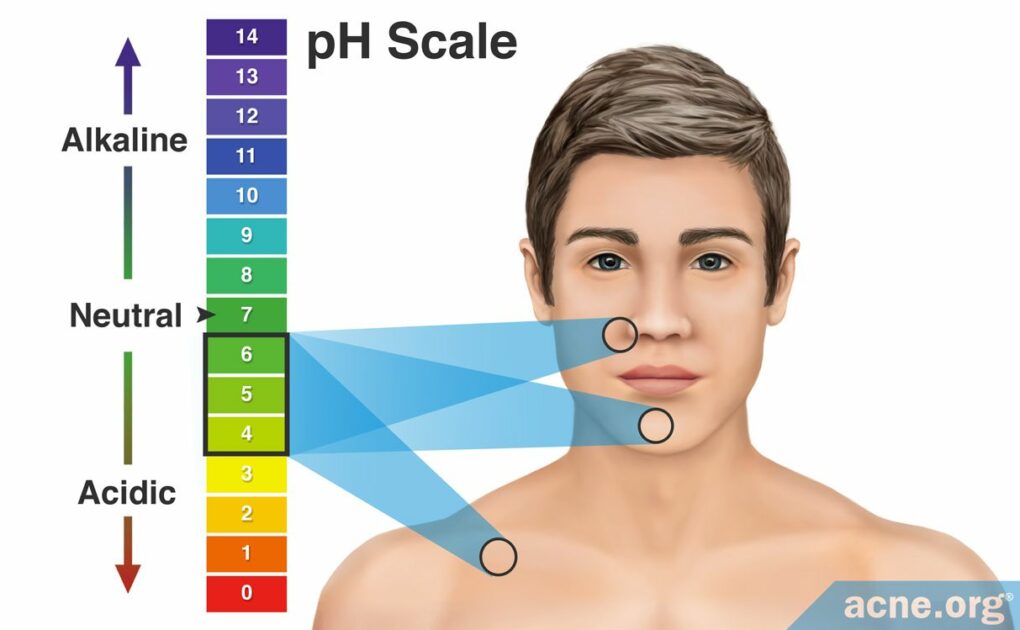
Human Skin Has an Average pH Value of Between 4 and 6, with Facial Skin Typically Having a pH Value of Between 4.5 and 5.5
The Essential Info
pH is the measure of how acidic or alkaline something is. Human skin has a pH that is slightly acidic.
A substance with a pH of 7 is considered neutral, and anything below 7 is acidic. Depending on where we look on the body, human skin has an average pH value of between 4 and 6, with facial skin typically having a pH value of between 4.5 and 5.5.
However, a variety of factors can impact the pH of a given person’s skin. For example, the skin’s pH value can change temporarily after water, cleansers, or skincare products have been in contact with the skin. The skin’s pH also tends to rise as people age.
Other suggested factors, such as gender and ethnicity, have not been studied well enough to say with certainty how they might impact the skin’s pH.
The Science
- The pH of Human Skin
- Scientific Studies Point to a pH Range of 4 – 6 for Human Skin
- Factors That Can Impact the Skin’s pH
- The Bottom Line
The term “pH” refers to a scale used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of something. The scale assigns each substance a pH value between 0 and 14 units, with a “neutral” pH being 7. The lower the pH value, the more acidic the substance is. Conversely, the higher the pH value, the more basic–or “alkaline”–the substance is. Substances with pH values under 7 are considered acidic, while those with pH values above 7 are considered alkaline. Examples of substances and their pH values are shown below.

The pH of Human Skin
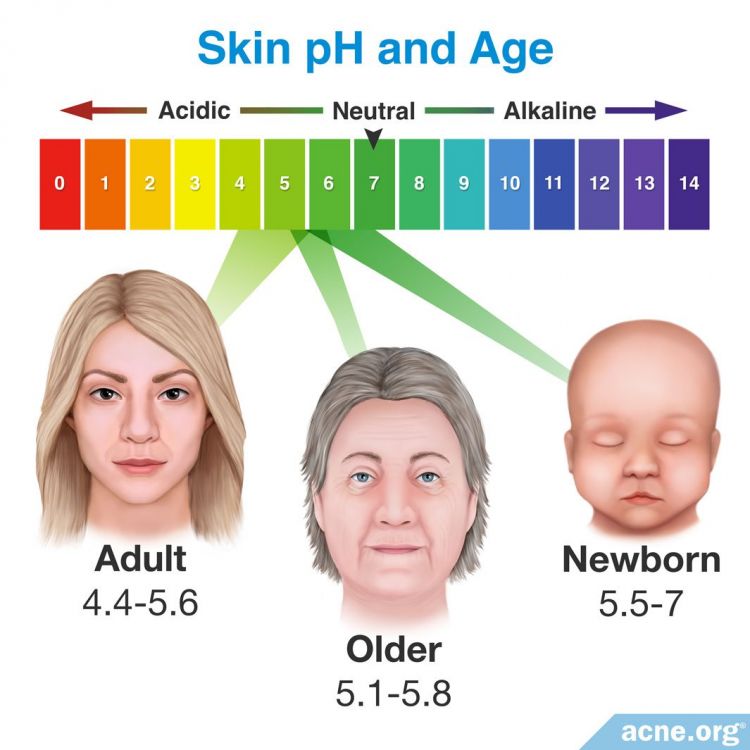
Human skin has its own pH value, but it varies between individuals, with the values ranging anywhere from 4 – 6. Facial skin normally falls within the 4.5 – 5.5 range. This means that the skin’s surface possesses the pH of a weak acid. The pH value of skin can also vary depending on its location on the body. For example, the forehead typically has the lowest pH value and the forearm, the highest.1 Even on the face itself, the skin’s pH varies. For example, the chin tends to have the highest pH value, around 5.5, and the forehead and upper eyelid tend to have the lowest pH values, around 4.5.2
Scientific Studies Point to a pH Range of 4 – 6 for Human Skin
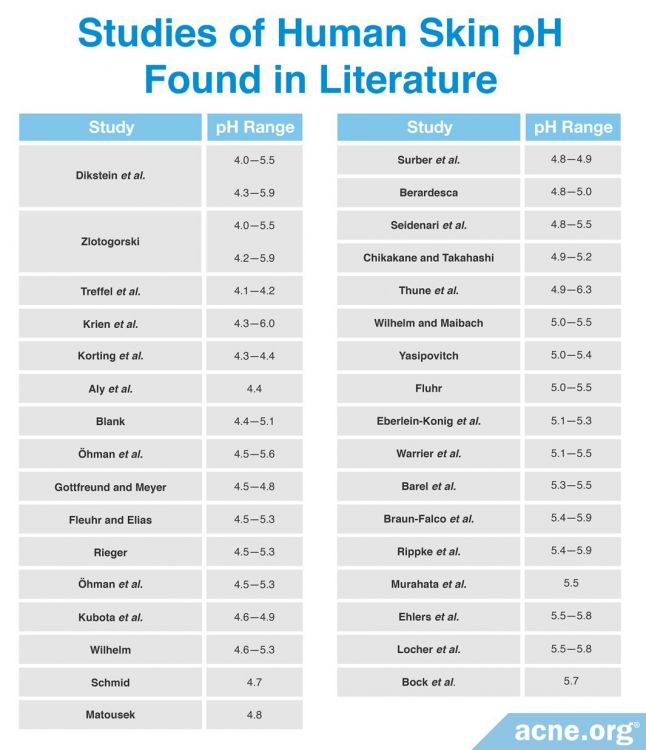
In the past, the general assumption was that skin has an average pH of between 5 and 6. However, more recent research-studies show that human skin has a broader average pH range of between 4 and 6.
Expand to read recent research

In a 2006 study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Science, researchers measured the pH of the internal surface of the forearm in 330 subjects. The subjects were asked to refrain from any contact with water or cosmetic products for 24 hours. Measurements were taken before and after the 24-hour period. The average initial pH value of the forearm skin was around 5.12. After 24 hours without contact with water or cosmetics, the average pH dropped to around 4.93. Based on this drop in pH, the researchers concluded that the skin’s average pH in its natural state is around 4.7. Other scientific studies, the majority of which also tested forearm skin, bore similar results, with pH values ranging anywhere from 4 – 6. The average was around 5.3
Factors That Can Impact the Skin’s pH
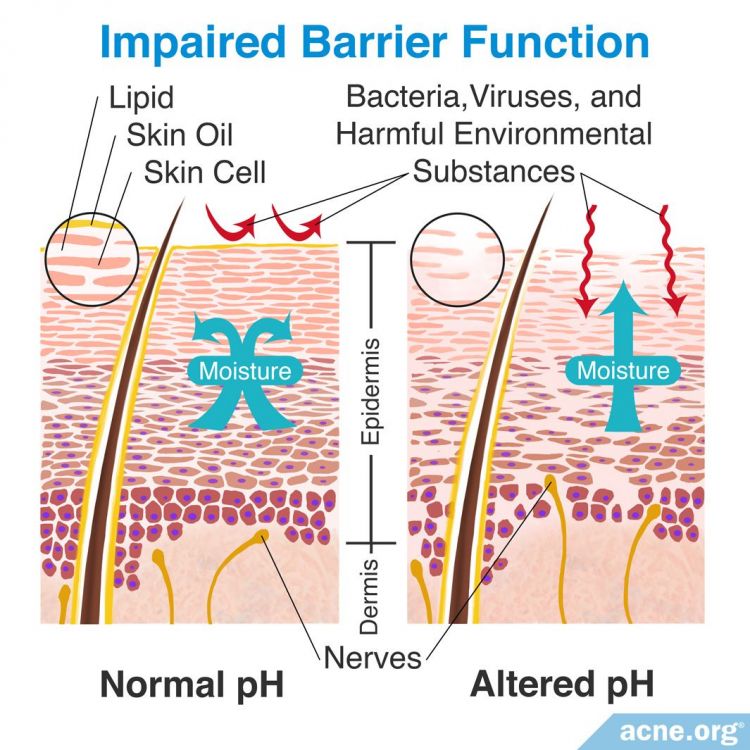
Maintaining a stable pH value is important for the wellbeing of the skin, and is of concern for people with acne as well. For example, the skin’s protective barrier can be weakened if the pH of the skin changes. People with acne tend to have an impaired protective barrier already, so it is best to keep the pH of acne-prone skin steady. Additionally, the balance of bacteria on the skin relies on a stable pH environment. Since acne is in part a bacterial disease, again, it is important to keep the pH stable to best fight bacteria.
Water
Water has a pH value of 7, so it is neutral. Because its pH value is higher than the skin’s, water can increase the skin’s pH levels when in contact with it. Simply washing the skin with water alone immediately causes a temporary increase in the skin’s pH value. This is unlikely to cause big problems, because a pH of 7 is not that far from an average skin pH, but as we will see, some cleansing products have higher pH values that could cause problems.
Cleansing products

Skin cleansing products can likewise change the skin’s pH value when applied.
Washing the hands with regular soap, which generally has an alkaline pH of 9 – 11, causes the pH on the palms to increase by 3 units, on average. In other words, if the pH was 5.5 before washing, it will go up to 8.5 after washing. This is only temporary, but it can take hours for the pH value to return to normal.
These changes in pH levels alter the balance of bacteria on the skin, slowing down the growth of some strains–including beneficial bacteria–and potentially boosting the growth of others. Based on a study published in Skin Pharmacology and Physiology in 2006, cleansing with an alkaline cleanser slightly increased acne, and cleansing with an acidic cleanser closer to the skin’s natural pH reduced acne. Was the slight increase in acne that the researchers found in the group of participants who washed with an alkaline cleanser due to acne bacteria flourishing in the higher pH skin environment? We don’t yet know this, but it is a potential explanation.

They studied two groups of individuals with mild-to-moderate acne who were instructed to apply either an alkaline soap or acidic facial cleanser to facial skin for one minute each morning and evening for a period of three months. In the group using alkaline soap, results showed an increase in inflammatory acne lesions, from 14.6 to 15.3. In the group using the acidic cleanser, acne lesions decreased, from 13.4 to 10.4. The researchers therefore concluded that acidic cleansers are more useful than regular alkaline soap in the treatment of acne.4
Age
Unlike water and cleansing products, which only change the pH of the skin in the short term, the aging process has a more lasting effect on the skin’s pH. This is particularly pronounced in the very young and the elderly, both of whom have a higher skin pH, as we see from the following two studies.
Expand to read details of studies

One study in Skin Pharmacology and Physiology in 2006 reported that surface pH values in infants went from neutral (around 7) at birth to around 5.5 within the first four days post-birth. This was likely due to the skin’s natural maturation and adaptation to new surroundings outside the womb. The same study showed no significant changes to the skin’s pH levels in subjects during adulthood.4

Another study, published in Archives of Dermatology in 1991, measured the pH values of the skin on various parts of the body in two groups of individuals: a younger group of 14 subjects, with an average age of 26.7 years, and an older group of 15 subjects, with an average age of 70.5 years. In the younger group, the mean pH varied from 4.8 on the ankle and forehead to 5.5 on the thigh. In the older group, the mean pH varied from around 5.1 on the forehead, ankle, and upper back to 5.5 on the abdomen. The study showed that skin pH on the forehead and ankle was significantly higher in the older age group than in the younger age group, but skin on other areas of the body showed little statistical difference.1
In another similar study, published in Contact Dermatitis in 2007, confirmed that older people tend to have a higher skin pH.
Expand to read details of study

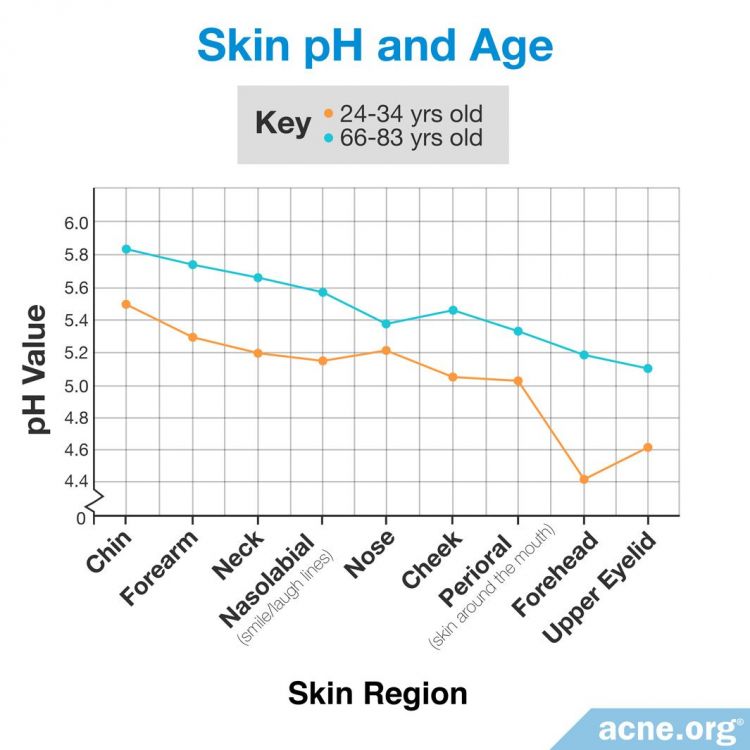
Scientists measured the pH values of skin on different areas of the forearm and face in 10 younger subjects, aged 24 – 34 years, and 10 older subjects, aged 66 – 83 years. The chin and forearm showed the highest pH values in both groups, whereas the forehead and upper eyelid showed the lowest pH in both groups. The younger group had an overall lower skin surface pH than the older group. Statistically significant differences between the two age groups were noted on the upper eyelid, forearm, neck, and forehead.5
Gender
Although anecdotal reports suggest that skin pH varies between different genders, only two studies that test for gender differences have been performed. However, these studies involve small sample sizes, and results are conflicting, so it cannot be concluded whether gender affects pH.
Expand to read details of studies

The first study looking at gender and the pH of skin, published in Skin Research and Technology in 2001, examined six men and five women, and reported that women had a lower skin pH than men. The women had a mean forearm surface skin pH of 5.54, and the men had a mean value of 5.8.2

On the contrary, a second study published in Skin Pharmacology and Physiology in 2006 looked at six men and six women and found a higher forearm skin pH value in women than in men, with women having a pH of 5.6 and men having a pH of 4.3.4 The results from these two studies show conflicting results. However, both studies evaluated only small groups of men and women, making the test results preliminary. Due to the small size of the study groups, one subject with an unusually high or low pH could have skewed the results for the entire group.
Ethnicity
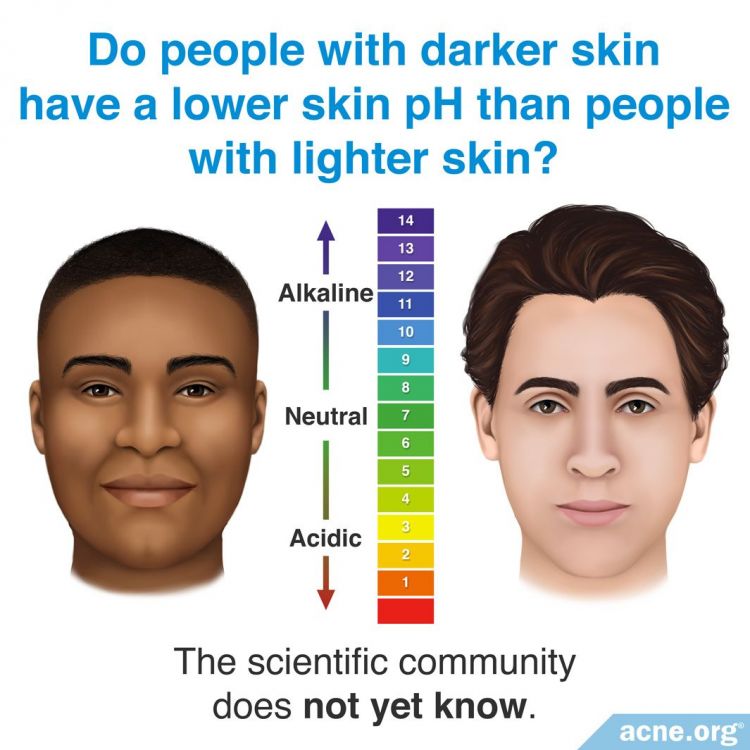
Ethnicity may play a role in differences in skin pH. For example, it has been demonstrated that individuals with darker skin have a lower skin pH than individuals with lighter skin. However, scientific studies using exact statistical methods have not proven this. We will need more research to show what impact, if any, ethnicity has on skin pH.4
The Bottom Line
Human skin, in general, tends to have a pH of 4 – 6, and facial skin tends to be between 4.5 and 5.5. It makes scientific sense to wash acne-prone skin with a cleanser that mimics the skin’s natural, slightly acidic, pH, and to avoid soap, which tends to have an alkaline pH. To find a cleanser that is slightly acidic, make sure you look for the words “facial cleanser” and/or “for acne-prone skin” on the label, and always avoid soap.
References
- Wilhelm, K. Skin aging. Effect on transepidermal water loss, stratum corneum hydration, skin surface pH, and casual sebum content. Arch Dermatol 127, 1806 – 1809 (1991). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1845280
- Ehlers, C., Ivens, U., Moller, M., Senderovitz, T. & Serup, J. Females have lower skin surface pH than men. A study on the influence of gender, forearm site variation, right/left difference and time of the day on the skin surface pH. Skin Res Technol 7, 90 – 94 (2001). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11393210
- Lambers, H., Piessens, S., Bloem, A., Pronk, H. & Finkel, P. Natural skin surface pH is on average below 5, which is beneficial for its resident flora. Int J Cosmet Sci 28, 359 – 370 (2006). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18489300
- Schmid-Wendtner, M. & Korting, H. The pH of the Skin Surface and Its Impact on the Barrier Function. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 19, 296 – 302 (2006). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16864974
- Marrakchi, S. & Maibach, H. Biophysical parameters of skin: map of human face, regional, and age-related differences. Contact Dermatitis 57, 28 – 34 (2007). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17577354
 Acne.org Products
Acne.org Products