Hypertrophic and keloid scars are raised scars that contain excessive collagen.
Verapamil is a drug that blocks calcium channels in the human body. When it is injected directly into a raised scar (“intralesionally”), it can stimulate collagen breakdown and decrease the production of new collagen. This helps reduce the size and thickness of the scar. The treatment can be painful and often requires multiple (up to 8) sessions.1,2
Because it is relatively safe and inexpensive, intralesional verapamil is sometimes used for the treatment of hypertrophic and keloid scars, but results are mixed, and sometimes it does not work at all. Some patients also stop treatment before obtaining the desired results due to pain.2
As with all scar revision treatments, intralesional verapamil is sometimes combined with other scar revision procedures to achieve the desired results.
Before agreeing to undergo intralesional verapamil treatment, discuss your options, expected outcomes, and prices with multiple doctors.
Procedure details:
Intralesional verapamil may help reduce scar size by:
- Stimulating collagen breakdown
- Decreasing collagen production
- Decreasing fibroblasts (cells that produce collagen)1-7
Verapamil, in the form of verapamil hydrochloride, is injected into the middle of the dermis, the deeper skin layer that is still intact underneath the raised scar. Injecting the drug into the middle of the dermis also reduces the chances of skin thinning (atrophy), which can be a side effect of intralesional verapamil.2
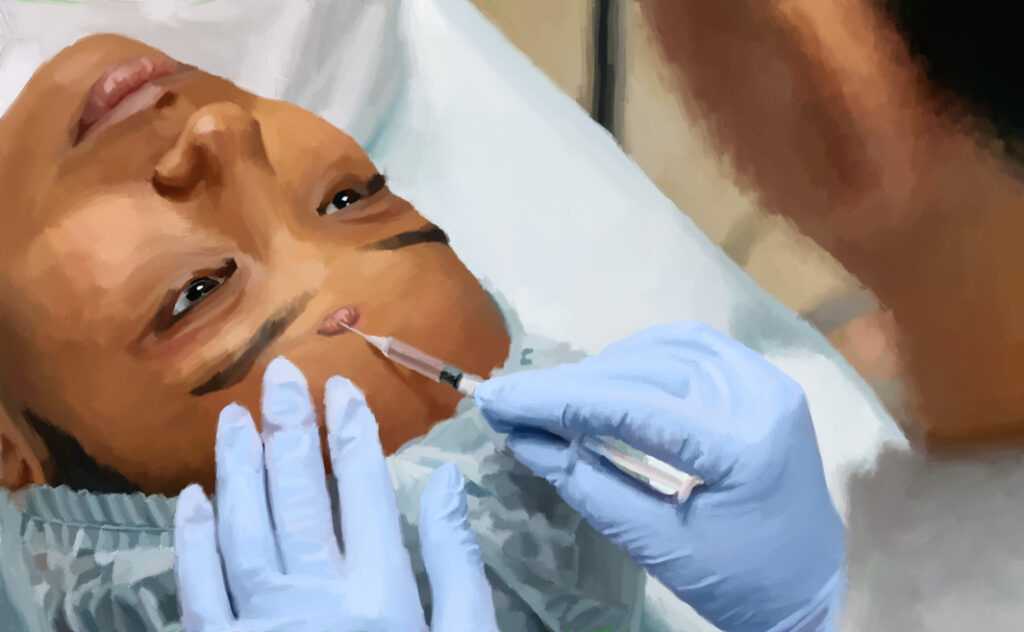
Depending on the extent of the scarring, your doctor may adjust several factors in intralesional verapamil treatment:
- Number of treatment sessions: Larger scars require more sessions than smaller scars. In general, up to 8 sessions are usually necessary for larger scars. If there is no improvement at all after 4 treatment sessions, treatment is normally stopped.
- Time between treatment sessions: The time between sessions can vary from 1 to 6 weeks, but is usually 3 weeks.
- Verapamil dose: The typical dose of injected verapamil is 2.5 mg/ml. Your doctor must weigh the efficacy of the treatment, which tends to increase with a higher dose, against the risk of side effects, which also increase with a higher dose.1,3
Anesthesia:
Before the treatment, the doctor may numb the scar using either:
- A topical numbing cream 30-60 minutes prior to the procedure
- An injection of a local anesthetic
Before-and-after:
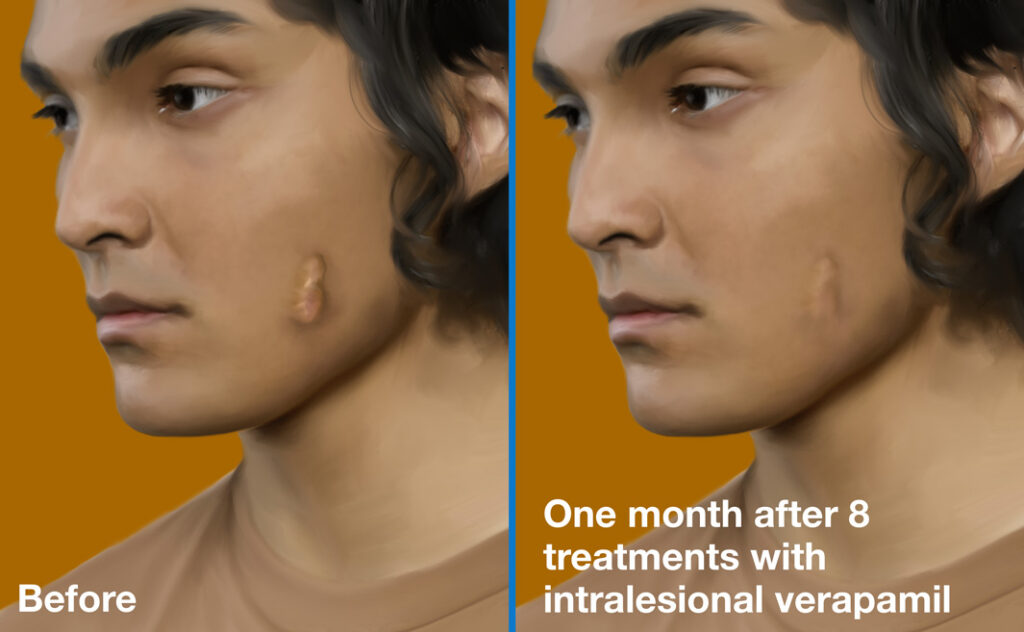
Before and one month after 8 treatments with intralesional verapamil
References
- Jiang ZY, Liao XC, Liu MZ, Fu ZH, Min DH, Guo GH. The Safety and Efficacy of Intralesional Verapamil Versus Intralesional Triamcinolone Acetonide for Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Adv Skin Wound Care. 33(4), 1-7 (2020).
- Ahuja RB, Chatterjee P. Comparative efficacy of intralesional verapamil hydrochloride and triamcinolone acetonide in hypertrophic scars and keloids. Burns. 40(4), 583-8 (2014).
- Abedini R, Sasani P, Mahmoudi HR, Nasimi M, Teymourpour A, Shadlou Z. Comparison of intralesional verapamil versus intralesional corticosteroids in treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars: A randomized controlled trial. Burns. 44(6), 1482-8 (2018).
- Margaret Shanthi FX, Ernest K, Dhanraj P. Comparison of intralesional verapamil with intralesional triamcinolone in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 74(4), 343-8 (2008).
- Belie O, Ugburo AO, Mofikoya BO, T Omidiji OA, Belie MF. A comparison of intralesional verapamil and triamcinolone monotherapy in the treatment of keloids in an African population. Niger J Clin Pract. 24(7), 986-92 (2021).
- O. Mohamed, R., M. Kamel, A., M. Mostafa, O., & A. Gadallah, N. EFFICACY OF INTRALESIONAL VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE VERSUS INTRALESIONAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE IN HYPERTROPHIC SCARS AND KELOIDS. Al-Azhar Medical Journal, 50(4), 2887-900 (2021).
- Wang R, Mao Y, Zhang Z, Li Z, Chen J, Cen Y. Role of verapamil in preventing and treating hypertrophic scars and keloids. Int Wound J. 13(4), 461-8 (2016).
 Acne.org Products
Acne.org Products