It Is Likely, Because Sleep May Help Balance Oil Production, Decrease Stress, and Support Wound Healing
The Essential Info
Although lack of sleep has not been proven to be a direct cause of acne, research shows that proper sleep encourages several things that could theoretically help prevent acne:
- Healthy skin oil production
- Stress reduction
- Wound healing (acne lesions are small wounds)
The Bottom Line: Getting adequate sleep won’t completely clear up acne, but it may help to some degree. Try to get 8 hours a night or more when you can.
The Science
Common sense tells us that getting enough sleep will help keep us healthy, and might even help reduce acne.
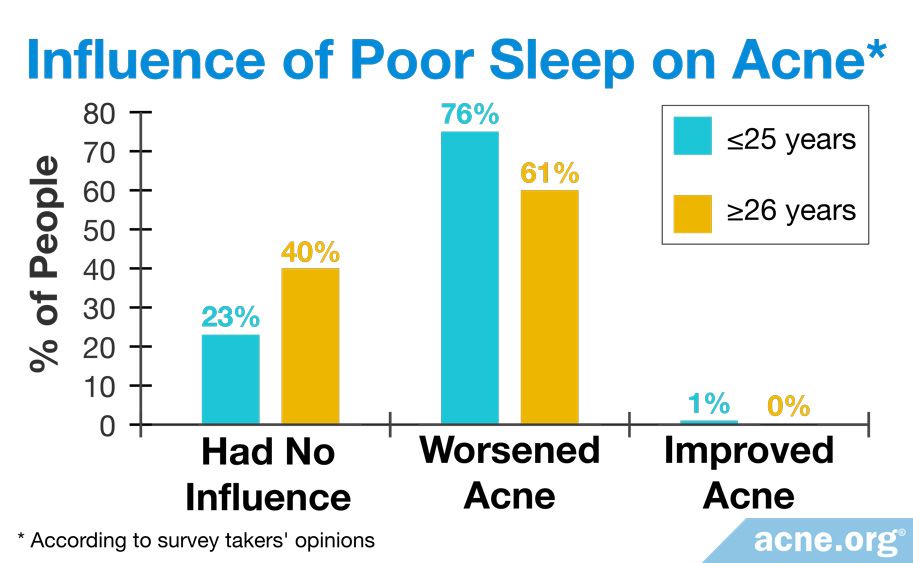
People with acne seem to agree, as reflected in the following survey results from a 2011 study published in the International Journal of Dermatology:

Among people who were surveyed about their acne, 76% believed that acne was triggered by poor sleep. Only stress was believed to be a greater factor, which was reported by 82% of people.1
Although many people believe that lack of sleep causes acne, this is not yet proven with direct scientific evidence. However, we do know that sleep is important for maintaining the health of the skin. Here’s what researchers in a 2016 study published in the Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology say about sleep and the skin:

“Sleep performs protective and restorative functions for the skin…Studies have suggested that acute sleep deprivation and poor sleep quality may impair the integrity of the skin.”2
How Getting Adequate Sleep Might Help Reduce Acne
The following are underlying factors that affect acne. Sleep also affects each of these factors in a positive way. Therefore, proper sleep might help reduce acne.
- Skin oil
How it affects acne: Problems with skin oil production can lead to acne
How sleep affects it: Sleep promotes healthy skin oil production - Stress
How it affects acne: Stress can make acne worse
How sleep affects it: Sleep reduces stress - Wound healing
How it affects acne: Acne lesions are small wounds and need to heal properly
How sleep affects it: Sleep promotes wound healing3
Let’s have a closer look at each of these factors one by one and see what the science says. It will get a little involved at times, so put on your thinking cap : )
Skin Oil
Generally speaking, there are two things to consider when it comes to skin oil and acne:
- More skin oil means more acne: Just about every study ever performed bears this out. It is accepted science.
- Altered composition of skin oil may also lead to acne: Research is now showing us that people who have acne have a different composition of skin oil compared to people without acne. A radically simplified way of looking at this is that the skin oil in people with acne has gone rancid.
So what happens to skin oil when we sleep? Researchers in India in 2016 put this question to the test when they studied 85 women. They found that skin oil production increased during sleep. This was a somewhat surprising finding. However, the researchers argued that even though production increased, the composition of the skin oil produced during sleep positively affected the skin in a manner that might reduce acne.2
Stress

Broadly speaking, the more stressed a person is, the more likely it is that he/she will develop more acne symptoms. This is likely because stress:
- Increases hormones called androgens (male hormones present in males and females) that are associated with acne
Poor sleep may disrupt hormonal cycles, leading to an increase in androgens.4,5 - Increases skin oil production (remember, more skin oil normally leads to more acne)
When we get stressed, the brain releases a specific hormone called corticotropin-releasing hormone. Corticotropin-releasing hormone leads to an increase in testosterone (an androgen hormone) around skin-oil-producing glands in the skin. The increase in testosterone around these glands causes the glands to increase in number, and in turn, more skin oil gets produced.5 - Weakens the body’s ability to repair wounds (remember, acne lesions are small wounds)
Stress can cause the body to release certain substances that block healing at the site of a wound.6 As researchers noted in a 2003 study published in Archives of Dermatology, “[P]sychological stress…can slow wound healing by up to 40%, which could be a factor in slowing the repair of acne lesions.”5
Sleep is one of the body’s most important ways to control stress. So it makes sense that getting enough sleep will help reduce stress and thus reduce acne.
Wound Healing
Since acne lesions are small wounds, we want them to heal them as quickly and effectively as possible.
Sleep directly helps with wound healing through the activation of:
- The immune system
Quick healing of acne depends on a fully functioning immune system. The immune response peaks during sleep and then drops when awake.4 In other words, a healthy immune system requires sleep. - Release of hormones
During sleep, the body releases hormones, such as growth hormone, that encourage immune cell activation and tissue growth, leading to skin healing at the site of a lesion.4,6,7 - Tissue regeneration
Animal studies have shown that the regeneration of skin and other tissues occurs mostly during sleep. In fact, new tissue growth happens about twice as fast during sleep than it does when awake. This is part of another cycle that corresponds to our sleep patterns. Tissue breakdown mostly occurs during waking hours and is balanced by tissue growth and repair that mostly occurs during sleeping hours.7 Since tissue regeneration is necessary for repairing skin damage caused by acne lesions, this is another reason why sleep is most likely very important for acne-prone people.
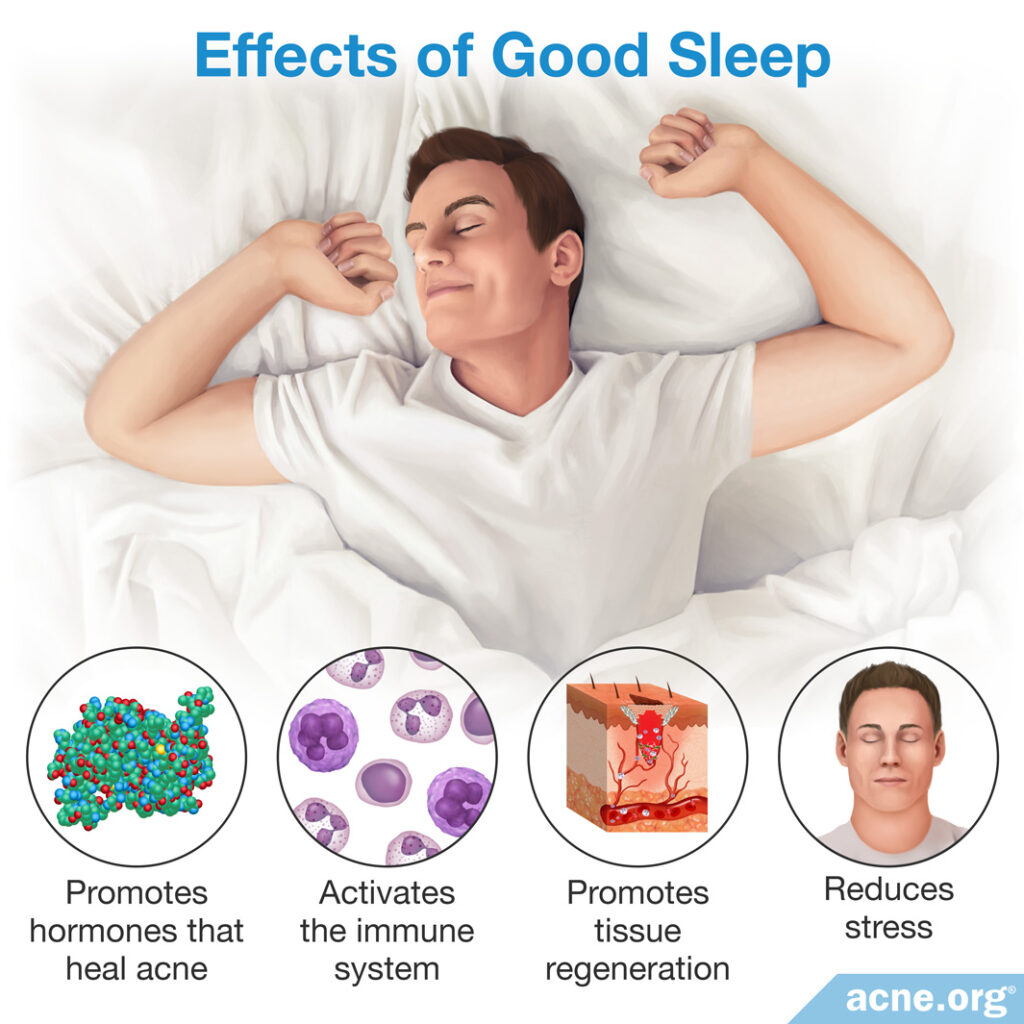
Conclusion
Insufficient sleep can lead to unhealthy skin-oil-production, hormone imbalances, increased stress, and can impair the skin’s ability to heal wounds. The combination of these factors may contribute to more acne, and cause slower healing and repair of existing acne lesions.
If we have to sum it all up in one sentence, here it is: Try to get eight hours or more of sleep per day when you can.
References
- Suh, D. H. et al. A multicenter epidemiological study of acne vulgaris in Korea. Int J Dermatol 50, 673-81 (2011). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21595660
- Bilgiç, Ö., Bilgiç, A., Altinyazar, H. C., Williams, H. C., Dellavalle, R. P. & Garner, S. Acne vulgaris. Relationship between sleep quality and facial sebum levels in women with acne vulgaris. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 82, 313-314 (2016). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27088937
- Williams, H. C., Dellavalle, R. P. & Garner, S. Acne vulgaris. Lancet 379, 361 – 372 (2012). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21880356
- Besedovsky, L., Lange, T. & Born, J. Sleep and immune function. Eur J Physiol 463, 121 – 137 (2012). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22071480
- Chiu, A., Chon, S. Y. & Kimball, A. B. The response of skin disease to stress: changes in the severity of acne vulgaris as affected by examination stress. Arch Dermatol 139, 897 – 900 (2003). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12873885
- Suh, D. H. & Kwon, H. H. What’s new in the physiopathology of acne? Br J Dermatol 172, 13 – 19 (2015). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25645151
- Adam, K. & Oswald, I. Protein Synthesis, Bodily Renewal and the Sleep-Wake Cycle. Clin Sci 65, 561 – 567 (1983). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6194928
